Over the past year, I’ve built and deployed several AI-powered services using tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and my own ML models. But after seeing Commonwealth Bank’s GenAI-focused job posting, I realized that to take my skills to the next level, I needed to understand a critical piece of the modern AI stack:
RAG – Retrieval-Augmented Generation
In this post, I’ll explain what RAG is, why it’s important, and how I built my very first RAG chatbot using LangChain, OpenAI, and FAISS. This project marks the first step in my deeper exploration of GenAI frameworks.
🧠 What is RAG?
LLMs like GPT or Gemini are trained on massive datasets, but their knowledge is static — they don’t know about your latest project, your internal documents, or any custom data.
That’s where RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) comes in.
RAG = Search + Generation. It combines a traditional search mechanism (like keyword or vector search) with an LLM to answer questions using external documents. Here’s how it works:
- Store Documents: Load and chunk your files (e.g., PDF, Markdown) into smaller pieces.
- Embed & Index: Convert chunks into vectors and store them in a database (like FAISS or Weaviate).
- Retrieve Relevant Context: When a user asks a question, search for the most relevant chunks.
- Generate Answer: Send those chunks to the LLM as context and generate an accurate response.
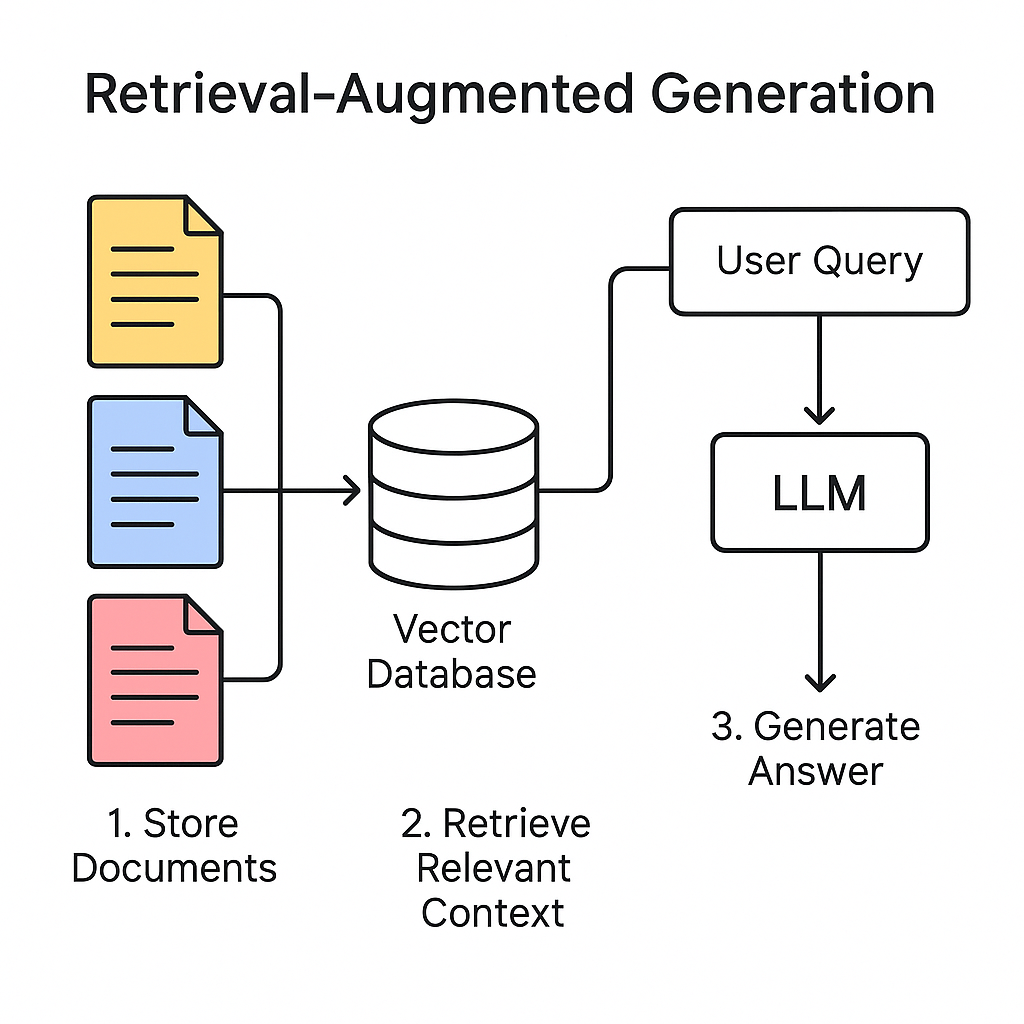
This makes your chatbot dynamic, searchable, and able to “read” real documents.
🧠 What is RAG? Building My First LangChain-based AI Chatbot with My Own Project Docs
Over the past year, I’ve independently built and deployed multiple AI-powered services using tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and my own ML models. But after seeing a job listing from Commonwealth Bank for a GenAI-focused Software Engineer role, I realized I needed to level up in one critical area of modern AI engineering:
🧩 RAG – Retrieval-Augmented Generation
In this post, I’ll walk you through what RAG is, why it’s important, and how I built my first RAG chatbot using LangChain, OpenAI, and FAISS – all centered around the actual README of one of my deployed projects. This marks a major step in my journey to align my work with the demands of next-generation AI-powered roles.
🧪 My Project: Chatbot for My Own README
I applied RAG to my own project’s README. The goal: build a chatbot that could understand and respond about my AI service — Before You Go, a globally targeted restaurant review summarizer for travelers.
🔧 Technology Used:
- LangChain – document processing + chain setup
- FAISS – local vector storage and similarity search
- OpenAI GPT-3.5 – answer generation
- .env + dotenv – secure API key handling
📄 Project README Summary (Indexed for QA)
Before You Go is a full-stack web service helping global travelers make informed dining decisions using AI-powered review summaries.
Built independently, it uses LLMs, RAG pipelines, and a mobile-friendly frontend with Supabase and Tailwind CSS.
Key technologies include LangChain, OpenAI, Gemini, FAISS, and GitHub Copilot.
It aligns with GenAI engineering practices by combining prompt engineering, real-time data search, and rapid deployment.
💬 Ask the Chatbot
After building the RAG pipeline, I asked the chatbot:
Q: What AI tools and frameworks are used in this project and for what purpose?
A:
In this project, the developer has used AI tools and frameworks such as LangChain, FAISS, OpenAI, Gemini (Google), Cursor, Copilot, and RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).
These tools serve various purposes like AI-assisted software development, retrieval-augmented generation for custom document search, prompt engineering for real-world integration, and rapid experimentation with large language models and vector search.
💻 My Sample Code
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
# Load API key from .env
load_dotenv()
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
# 1. Load document
loader = TextLoader("README.txt")
documents = loader.load()
# 2. Split into chunks
splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50)
docs = splitter.split_documents(documents)
# 3. Create embeddings and store in FAISS
embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
db = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embedding)
# 4. Setup Retrieval-based QA chain
retriever = db.as_retriever()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0.2, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, retriever=retriever)
# 5. Ask a question
query = "What AI tools and frameworks are used in this project and for what purpose?"
answer = qa_chain.run(query)
print("✅ Loaded Key:", openai_api_key[:6] + "..." if openai_api_key else "❌ Key not loaded")
print(f"Q: {query}")
print(f"A: {answer}")
💻 Code Walkthrough: Step-by-Step with Explanation
# 📌 Load environment variable
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
print("✅ Loaded Key:", openai_api_key[:6] + "..." if openai_api_key else "❌ Key not loaded")
🔍 Securely load your OpenAI key from a .env file using dotenv.
# 📄 Load the README document
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
loader = TextLoader("README.txt")
documents = loader.load()
🔍 Use TextLoader to load plain text files into LangChain.
# ✂️ Split the document into chunks
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50)
docs = splitter.split_documents(documents)
🔍 Split your text into overlapping chunks for better search and context.
# 🧠 Create embeddings and store in FAISS
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
db = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embedding)
🔍 Create vector embeddings of the chunks and store them in FAISS for efficient similarity search.
# 🔗 Setup a Retrieval-based QA chain
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
retriever = db.as_retriever()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0.2, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, retriever=retriever)
🔍 Create a QA pipeline using an LLM and vector-based document retriever.
# ❓ Ask a question and print the answer
query = "What AI tools and frameworks are used in this project and for what purpose?"
answer = qa_chain.run(query)
print(f"Q: {query}")
print(f"A: {answer}")
🔍 Send a question through the pipeline and receive a context-aware response.
✅ What I Learned
- RAG gives static LLMs dynamic awareness of any project or document.
- Tools like LangChain + FAISS make this surprisingly easy to implement.
- This approach is highly relevant to jobs in GenAI engineering, including those at Commonwealth Bank and beyond.
📌 What’s Next
- Expand to multi-document chatbots (e.g. PDF support, full wikis)
- Explore cloud vector DBs like Weaviate for scaling
- Integrate Agentic AI chains using LangGraph or AutoGen
- Bundle this chatbot into my React Native app
🇰🇷 한글 요약
이 블로그에서는 LangChain과 OpenAI, FAISS를 이용해 나의 프로젝트 문서를 이해하는 AI 챗봇을 만드는 과정을 소개합니다.
RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation)는 외부 문서 검색과 GPT 답변을 결합한 최신 AI 구조입니다.
📌 실습에서 사용한 내 README는 내가 개발한 ‘Before You Go’ 서비스로,
여행자에게 구글 리뷰 요약을 제공하는 AI 기반 글로벌 맛집 요약 플랫폼입니다.
🧠 질문 예시:
“이 프로젝트에 어떤 AI 도구와 프레임워크가 사용되었고 어떤 목적을 가지고 있습니까?”
→ LangChain, FAISS, OpenAI, Gemini, Copilot 등이 실제 문서 검색, 프롬프트 설계, 생산성 향상 목적에 사용됨.
이 과정을 통해 GenAI 기반 개발자 역량과 문서 기반 QA 챗봇 구현의 핵심 기술을 모두 경험했습니다.
'AI Study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 반드시 알고가자! (0) | 2025.06.04 |
|---|---|
| Step 2: Expanding RAG – Multi-Document Chatbot with PDF Support (0) | 2025.06.04 |
| Embracing the New Era of Development: Why AI-Native Engineering is My Path (0) | 2025.05.30 |
| 프로그래밍 수학 - 확률과 선형대수, 어디에 쓰일까? (0) | 2025.03.30 |
| 알고리즘과 수열, 그리고 파이썬과 인공지능의 연결 (0) | 2025.03.26 |